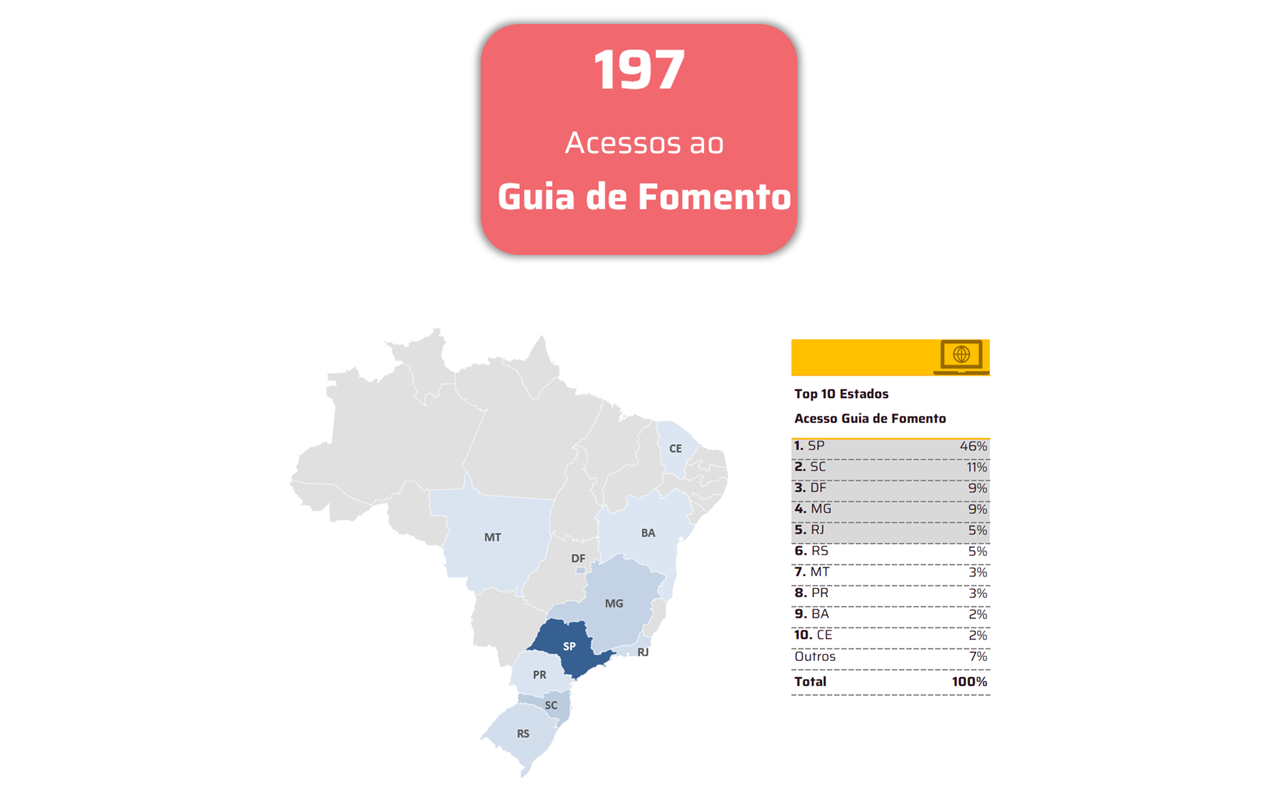
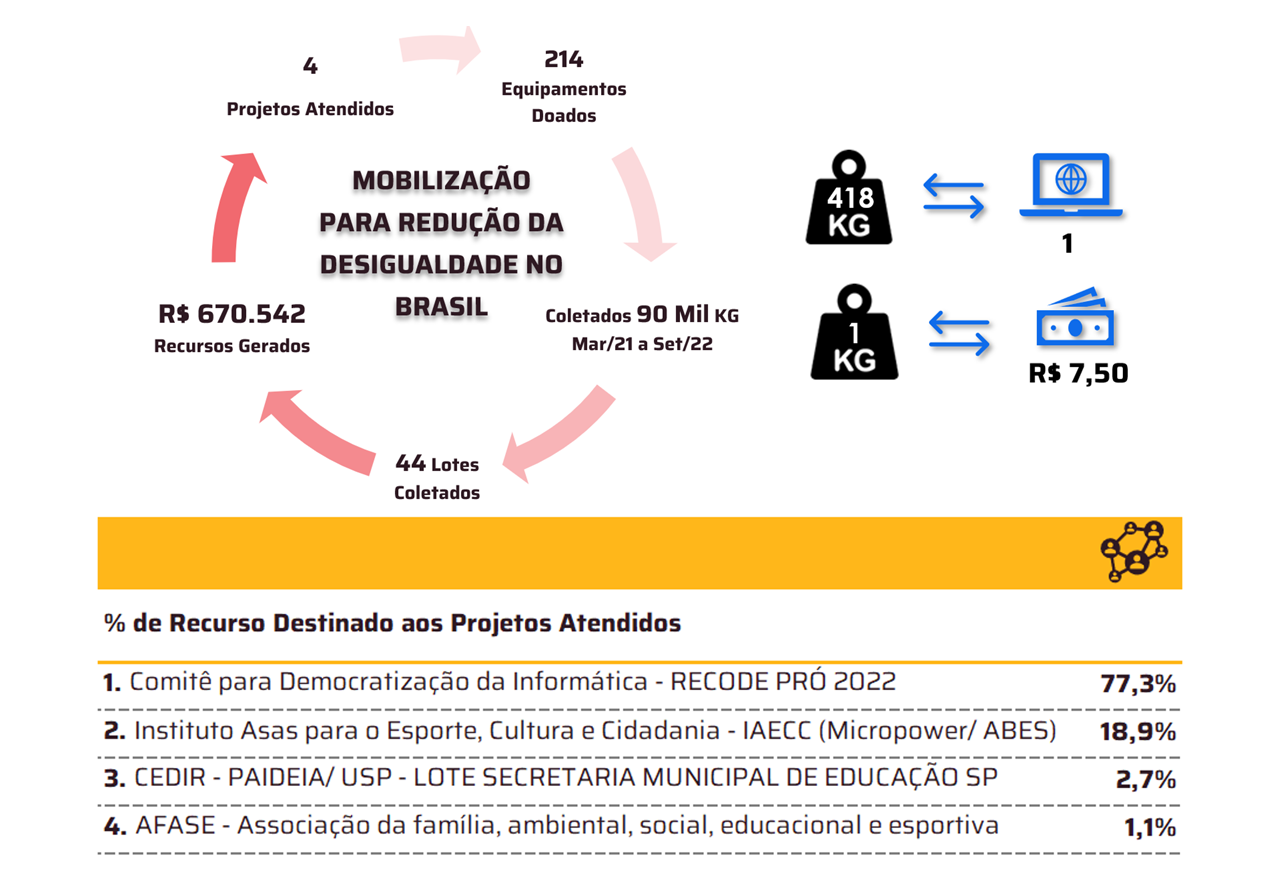
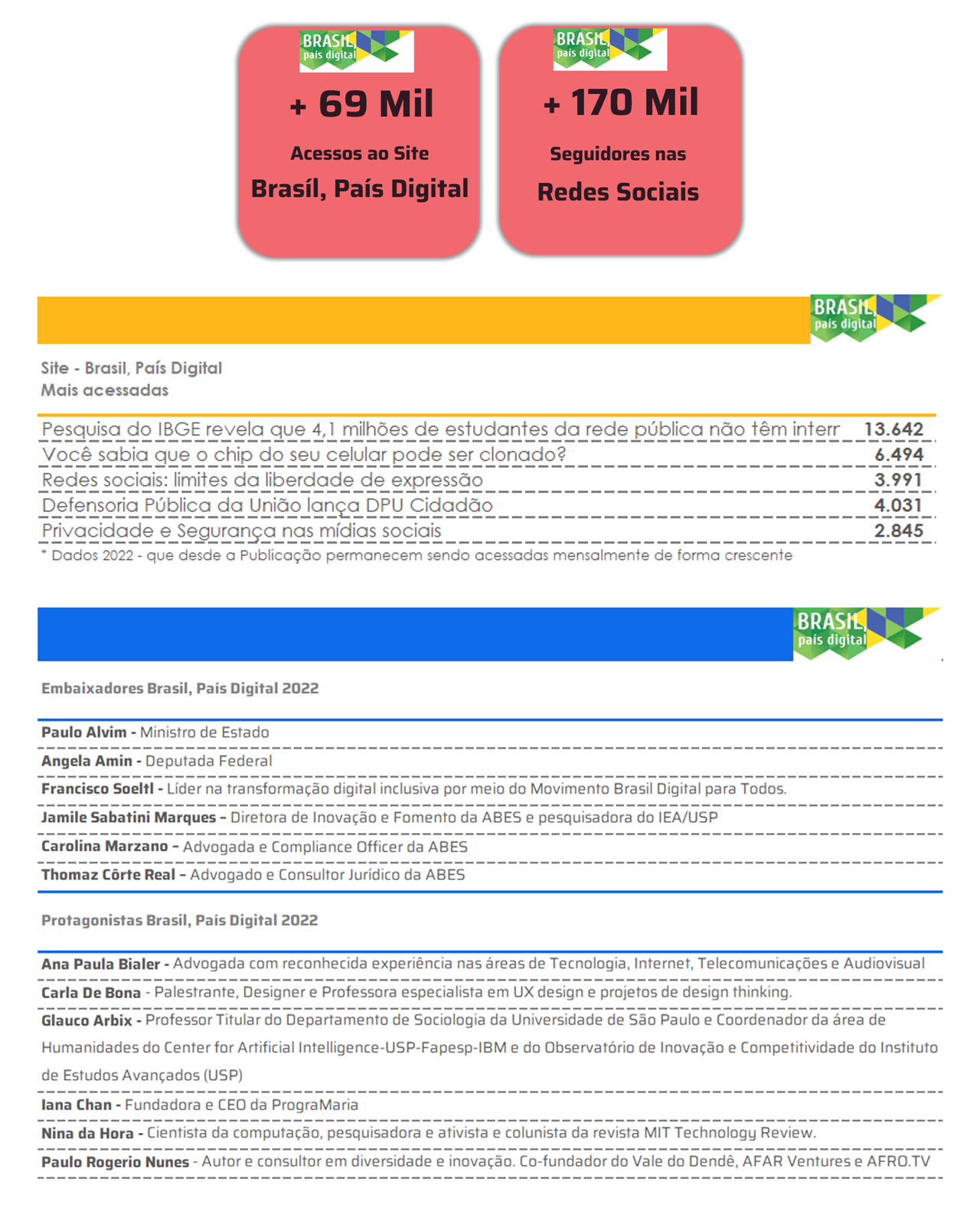
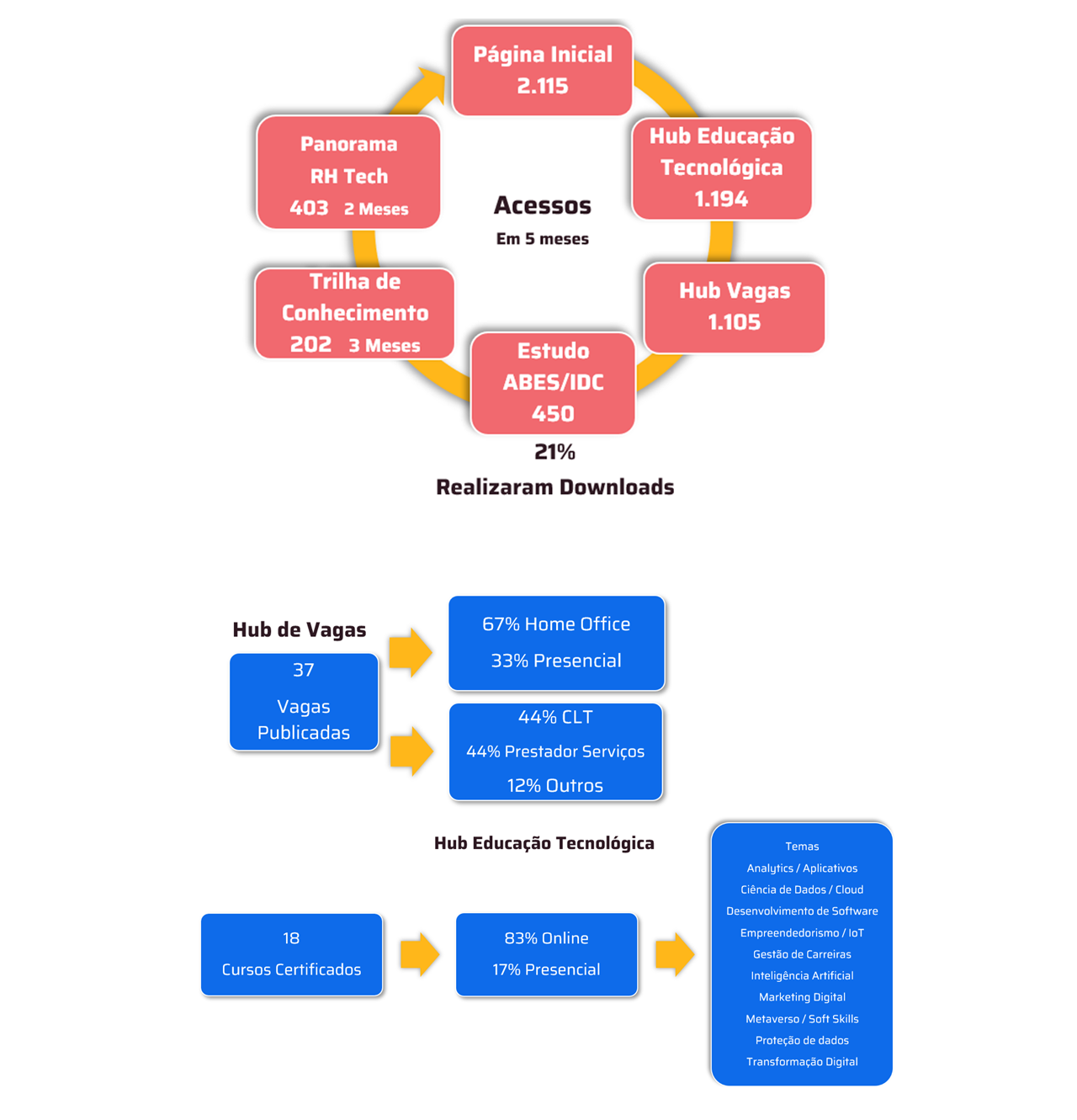
This is the first foundational heliophysics AI model trained on high-resolution solar observation data and offers insights into the Sun's dynamic surface.
IBM (NYSE: IBM) and NASA today unveiled the most advanced open-source foundational model designed to understand high-resolution solar observation data and predict how solar activity affects Earth and space technology. Surya, named after the Sanskrit word for Sun, represents a significant advancement in the application of AI to solar imagery interpretation and space weather forecasting research, providing a new tool to help protect resources and tools, from GPS navigation to power and telecommunications networks, from the ever-changing nature of the Sun.
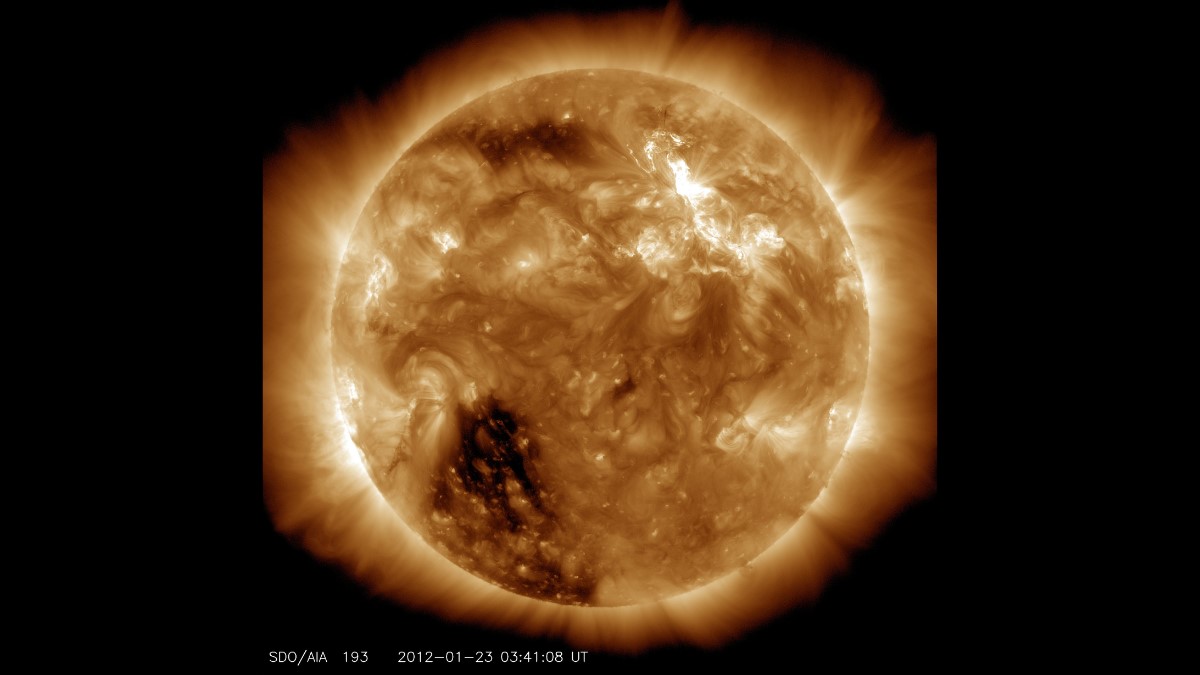
The Sun may be 93 million miles away, but their impact on modern life is immediate and growing. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections can knock out satellites, disrupt air navigation, cause power outages, and pose serious radiation risks to astronauts. With humanity's growing reliance on space technology and plans for deeper space exploration, accurate solar weather forecasting has become essential.
As humanity's dependence on technology grows, so does our vulnerability to space weather. According to a systemic risk scenario created by Lloyd's, the global economy could be exposed to losses of US$1.4 trillion over a five-year period, with an expected loss of US$1.4 trillion due to the threat of a hypothetical solar storm. Recent solar events[1] have already demonstrated the risk, disrupting GPS services, forcing flight diversions, and damaging satellites. The effects of solar storms can cause:
- Damage to satellites, spacecraft and/or astronauts that are stationed outside of Earth;
- Loss of satellite hardware, damaging solar panels and circuits;
- Impact on air travel due to navigation errors and potential radiation risk to airline crew and passengers;
- Reduced food production as agriculture may be affected by disruption of GPS navigation.
The implications include both academic research and operational preparedness. The new model will provide tools to help experts plan for solar storms, which can disrupt Earth's technological infrastructure.
"Think of it as a weather forecast for space," said Juan Bernabe-Moreno, director of IBM Research Europe, UK, and Ireland. "Just as we work to prepare for dangerous weather events, we need to do the same for solar storms. Surya gives us an unprecedented ability to anticipate what's coming and is not just a technological achievement, but a critical step toward protecting our technological civilization from the star that sustains us."
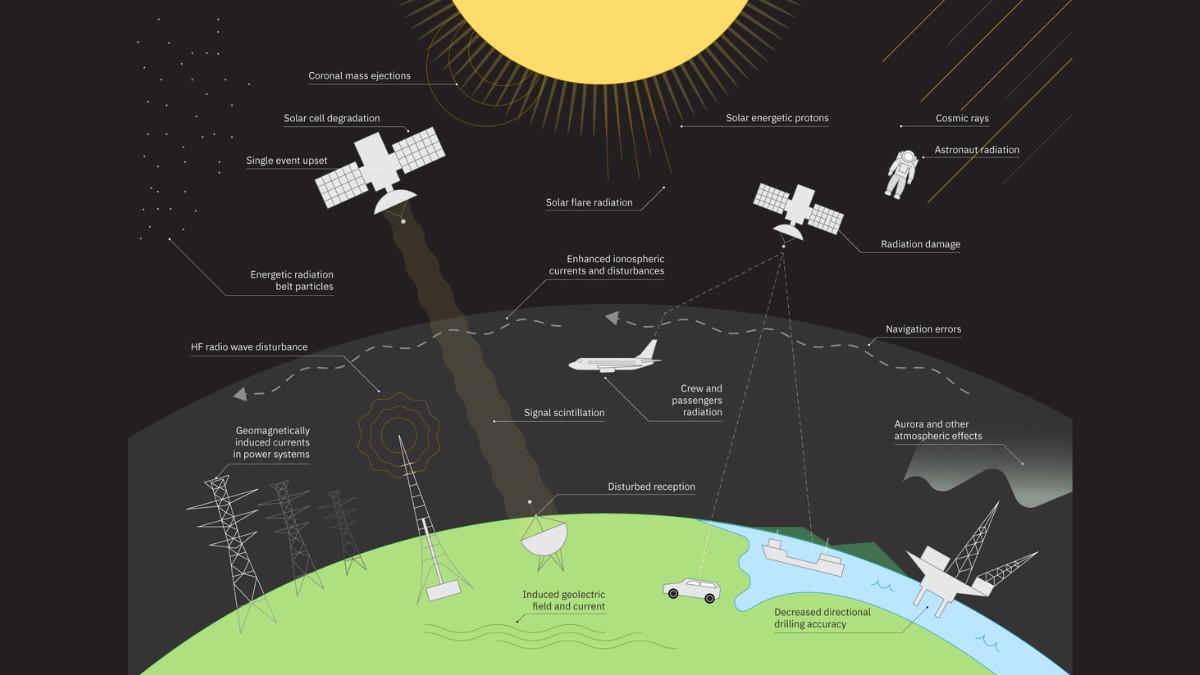
Traditional solar weather forecasting relies on partial satellite views of the Sun's surface, which has historically made accurate predictions extremely difficult. Surya addresses this typical limitation by being trained on the largest high-resolution dataset ever curated. This dataset was created to help researchers better study and evaluate critical space weather forecasting tasks. Examples of these tasks, on which Surya has been tested, include predicting solar flares, solar wind speeds, solar EUV spectra, and the emergence of active regions on the Sun.
In initial tests, the researchers reported a 16% improvement in solar flare classification accuracy, which they describe as a substantial improvement over previous methods. In addition to classifying binary solar flares, Surya was created to visually predict solar flares for the first time, providing a high-resolution image of where the flare is expected to occur up to two hours in advance.
The technical challenges were immense. Surya was trained on nine years of high-resolution solar observation data from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. These solar images are 10 times larger than typical AI training data, requiring a custom multi-architecture solution to handle the massive scale while maintaining efficiency. The result is a model with unprecedented spatial resolution that can resolve solar features at scales and contexts not previously captured in large-scale AI training workflows.
“We are advancing data-driven science by incorporating NASA’s deep scientific expertise into cutting-edge AI models,” said Kevin Murphy, director of Data Science at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “By developing a foundational model trained on NASA’s heliophysics data, we are facilitating the analysis of the complexities of the Sun’s behavior with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This model enables a broader understanding of how solar activity impacts critical systems and technologies that we all depend on here on Earth.”
Surya is part of a broader IBM effort to embrace generative and automated approaches that empower algorithms to be discovered, tested, and developed at scale. Surya is an example of how IBM is positioning AI not just as a tool, but as a driver of scientific discovery. By launching Surya in Hugging FaceIBM and NASA are democratizing access to advanced tools for understanding and predicting solar climate and scientific exploration. Researchers around the world can now leverage this foundation to develop specialized applications for their regions and industries.
This model is part of a larger collaboration between IBM and NASA to use AI technology to explore our planet and solar system. It joins to the Prithvi family foundational modeling suite, which includes a geospatial model and a climate model. Last year, IBM and NASA launched the Prithvi climate model at Hugging Face for scientists and the community at large to develop short- and long-term climate and weather projections.
About IBM
IBM is a leading global provider of hybrid cloud and AI, as well as consulting expertise. We help clients in more than 175 countries capitalize on insights from their data, optimize business processes, reduce costs, and gain competitive advantage in their industries. Thousands of governments and corporate entities in critical infrastructure areas such as financial services, telecommunications, and healthcare rely on IBM's hybrid cloud platform and Red Hat OpenShift to impact their digital transformations quickly, efficiently, and securely. IBM's breakthrough innovations in AI, quantum computing, industry-specific cloud solutions, and consulting offer open and flexible options to our clients. All of this is backed by IBM's long-standing commitment to trust, transparency, accountability, inclusion, and service.
[1] Causes and Interplanetary Impacts of the May 2024 Superstorm on the Geosphere: Overview – IOPscience. Causes and Interplanetary Impacts of the May 2024 Superstorm on the Geosphere: Overview, Hajra, Rajkumar, Tsurutani, Bruce Tsatnam, Lakhina, Gurbax Singh, Lu, Quanming, Du, Aimin. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/ad7462